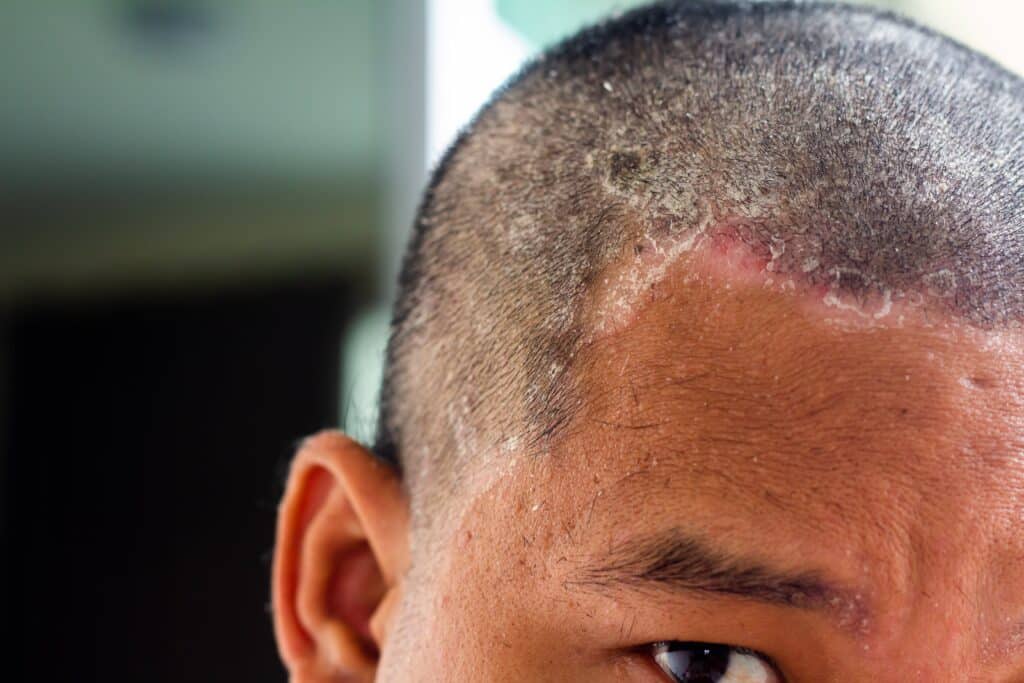
If your hair falls out in circles, or if your scalp turns red and flaky and there is severe itching, you may have a form of fungus that develops on the scalp. If you have scalp fungus hair loss, a visit to the dermatologist for medical advice is advisable.
All these skin conditions could be an indication of a so-called scalp fungus. Children are often affected, but adults can also suffer from a fungal disease that affects the scalp. This is because skin fungi in particular feel extremely comfortable in the warm and humid conditions which can occur under the hair.
The fungus tinea capitis is often responsible for fungal diseases of the scalp. This disease, also known as ringworm of the scalp, spreads highly contagiously from person to person. It transmits either directly or indirectly through contaminated objects.
A weakened immune system, injuries to the scalp, or bacterial infections, can also cause the fungus to colonise more quickly.
Microsporum canis, another common scalp fungus, transmits through dogs, cats, and guinea pigs.
Why you should treat scalp fungus
Medical treatment is necessary for a fungal scalp disease as it doesn’t heal on its own. Rather, the opposite can be the case. All these types of fungus can result in hair loss.
The first noticeable signs typically include patches of hair loss concentrated in the infected areas. The fungus can continue to spread and, in the worst case, can even enter the bloodstream. From there, it could also infect internal organs.
Furthermore, scalp fungus is highly contagious. It is therefore possible to infect family members or friends with the fungus completely unintentionally. Skin fungi thrive excellently in the warm, moist climate of the scalp and feed on microscopic skin flakes that abound there.
Scalp fungus is a medical condition. A visit to the doctor, in this case a dermatologist, is therefore absolutely necessary!
Don’t worry: a fungal skin infection is not a sign of poor hygiene!
Transmission prevention of scalp fungus and hair loss
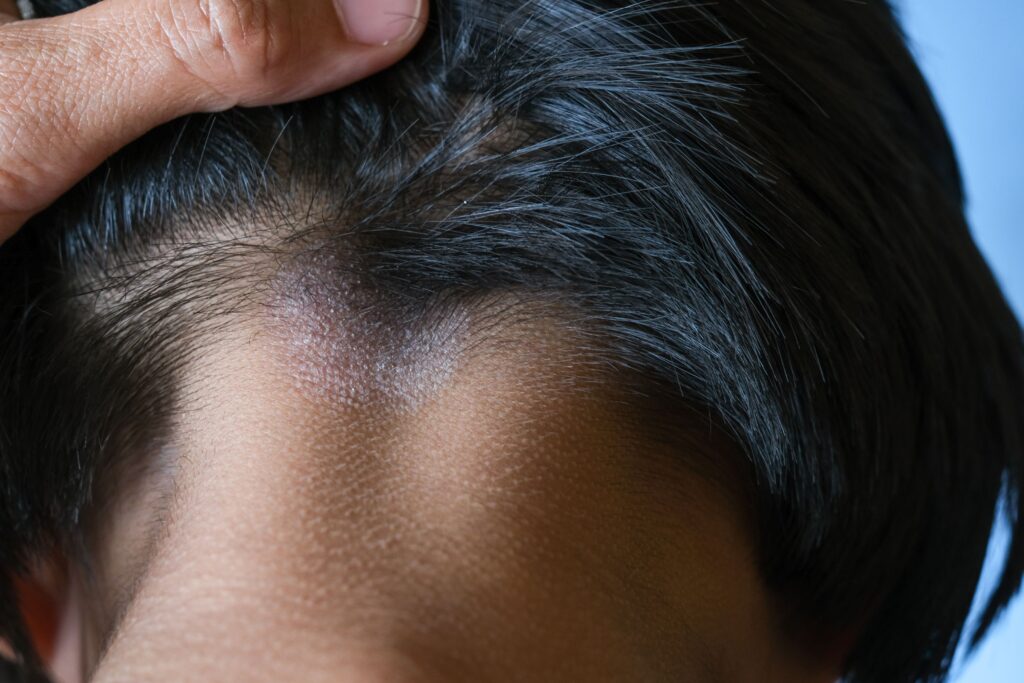
- Avoid sharing combs, hairbrushes, towels, and razors.
- Also don’t share bed linen, caps, scarves, etc.
- Regularly disinfect combs, scissors, towels, razors, etc., after treatment initiation. If feasible, boil-wash bed linen, and regularly disinfect or wash toys and cuddly toys at high temperatures.
- Additionally, it’s advisable to store all the mentioned items separately and regularly disinfect surfaces since fungi are notoriously resilient.
- During the infection, the affected person should actively avoid close contact with pets.
- During this time, it’s crucial to actively avoid visiting the hairdresser until the fungus has completely disappeared.
- Additionally, ensure to blow-dry the hair thoroughly after each wash. Fungi thrive in moist environments, so keeping the scalp dry helps prevent their growth.
- In case of microsporum canis, it’s essential to promptly have the pets examined by a vet. Also, disinfect or replace baskets, blankets, etc., to prevent further spread.
Other types of fungus that can infect the scalp
Most infections with skin fungi are caused by the so-called dermatophytes, which are a specific fungal infection of the skin. Tinea capitis and microsporum canis are examples of this type of fungus.
However, yeast fungi can also infect the scalp and thus lead to hair loss.
The genus malassezia belongs to the yeast fungi, which in fact occurs naturally on healthy skin, including the scalp. However, it can happen that these yeasts suddenly multiply uncontrollably due to certain circumstances, for example in the presence of a weakened immune system.
Typical symptoms of this are:
- Yellowish greasy dandruff
- Itchy patches that are usually reddish-brown in colour
- Increased hair loss
Malassezia is one of the triggers of the so-called seborrheic dermatitis, a skin rash that can appear on the head or face.
Another type of head fungi is trichosporon. With this fungus, small nodules form near the hair follicles. In particularly severe cases, the hair shaft can break off, which in turn leads to increased hair loss.
Regardless of the type of fungus infected you, it’s crucial to ensure that a competent doctor in the field handles scalp fungus hair loss.
Scalp fungus hair loss - symptoms and treatment
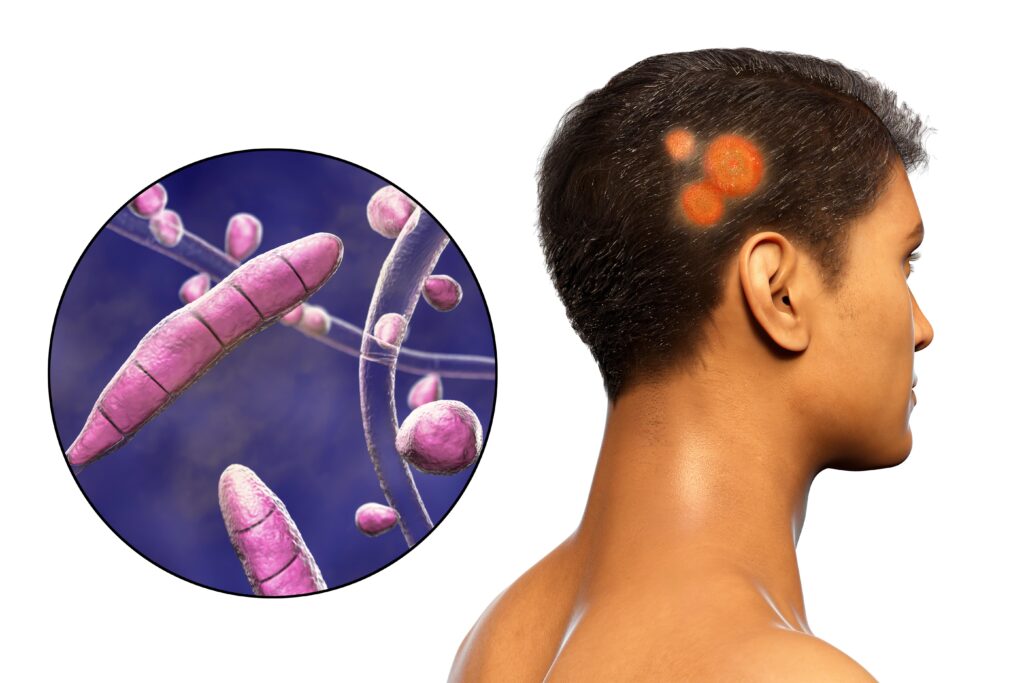
A fungal infection of the scalp causes severe itching. This is accompanied by a scaly and reddened scalp. In the further course, round, bald patches develop.
After taking the patient’s medical history, the dermatologist will take a skin and hair sample. Laboratory prepares a culture based on these samples to determine the responsible fungus for the infection.
Upon clear identification, doctors typically prescribe antifungal antimycotics, which are mainly administered orally. Additionally, they often recommend using special shampoos and tinctures on the affected areas for comprehensive treatment. Treatment takes place over a period of at least three months until complete healing.
Accompanying this, certain home remedies can also be used, such as some apple cider vinegar, turmeric, or garlic, which support healing.
However, treatment with home remedies alone is not enough to fight the fungus successfully and sustainably.
Will the hair loss grow back?
The good news at this point is: scalp fungal infections doesn’t cause permanent hair loss. In most cases, hair growth resumes after overcoming a fungal infection.
If they do not, it may be that the hair loss caused by the fungus has simply uncovered pre-existing hair loss problems such as genetic hair loss. A hair transplant in Turkey may be the solution to fill in the remaining bald spots.
However, the basic prerequisite for such an operation is that you have completely cured from the skin fungus, and that a qualified hair doctor deems it helpful.
FAQ
Symptoms of scalp fungus hair loss include severe itching, redness, flakiness, and the development of circular bald patches on the scalp. These symptoms signal the presence of a fungal infection, necessitating prompt medical attention.
Scalp fungus can be transmitted through direct contact with an infected person or indirectly through contaminated objects like combs, towels, or bedding. Additionally, certain types of scalp fungus can be transmitted by pets, emphasizing the need for caution during an infection.
To prevent transmission, avoid sharing personal items, regularly disinfect objects, wash bedding in hot water, and keep surfaces clean. Limiting contact with pets during infection and refraining from visiting hairdressers can also help prevent spread.
Besides dermatophytes like tinea capitis and microsporum canis, yeast fungi such as malassezia can infect the scalp, leading to symptoms like greasy dandruff and increased hair loss. Trichosporon is another fungus that can cause small nodules near hair follicles and exacerbate hair loss.
Yes, typically hair regrows after successful treatment of scalp fungus. However, if hair loss persists, it may indicate underlying issues such as genetic hair loss, requiring further evaluation by a hair doctor for potential solutions.