Androgenic alopecia is a hereditary hair loss condition that can affect men and women all over the world. It can manifest as male pattern baldness or, less commonly, as female pattern hair loss.
Despite the rarity of female pattern baldness, this genetic and hormonal-influenced condition can result in hair thinning, loss, and eventual balding in both genders. It is generally characterized by a receding hairline in men or a diffuse thinning over the crown for both men and women. In this blog post, we will focus our lens on the topic of hair loss in men and illustrate some possibilities.
What Are the Different Types of Hair Loss?
There are two main types of hair loss: Cicatricial alopecia and non-cicatricial alopecia. In Cicatricial alopecia, damaged follicles are replaced with fibrotic scar tissue, causing permanent hair loss. It is classified into two groups: Primary cicatricial alopecia (PCA) and secondary cicatricial alopecia (SCA).
Non-cicatricial alopecia, on the other hand, is a theoretically reversible alopecia characterized by an altered hair cycle and preserved hair follicles. They are divided into local alopecia and diffuse alopecia. Male pattern baldness or androgenic alopecia usually falls under diffuse alopecia. Types of diffuse alopecia commonly include:
- Androgenic alopecia: This type of baldness generally manifests when the hair follicle shrinks. It is the most common type of hair loss in men and women.
- Diffuse alopecia areata: This autoimmune disorder is the second most common type of non-cicatricial alopecia, causing hair loss from head to body.
- Telogen effluvium: Hormonal changes or side effects of extreme physical and emotional stress can cause this type of hair loss. People can lose their hair very suddenly and witness a receding hairline.
- Anagen effluvium: This type of hair loss occurs due to complex medical treatments such as chemotherapy, inflammation, etc.
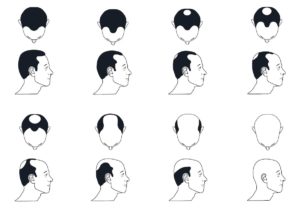
What Are the Stages of Male Pattern Baldness?
According to the Norwood scale, which is used by doctors to classify hair loss, there are seven stages of male pattern baldness. These stages also highlight the symptoms of androgenic alopecia:
Stage 1: Baldness is completely absent at this stage. Your hairline can naturally be high or low; it would not indicate a recession of your hair.
Stage 2: There’s a slight 1 to 2 cm recession at the temples.
Stage 3: The hairline takes an “M” or “U” shape. Slowly, the frontal hairline retreats, or there’s a bald spot gradually appearing in the center of the skull.
Stage 4: There is a visible hairline on the temples, but the upper portion of the head loses almost all the hair.
Stage 5: Hairline recession continues except on the sides and the back.
Stage 6: Hair is completely recessed on the crown of the head and a cluster of hair is connected from the side to the back.
Stage 7: The top of the head shows a complete bald spot, sometimes only a thinning hairline from side to back of the head may remain.
What Are the Causes of Male Pattern Baldness?
If you are someone with male pattern baldness, you may be wondering: Why me? What is the cause? Unfortunately, some genetic and hormonal factors can exacerbate this condition in some people. Some simple and diagnosed reasons for this type of hair loss can include:
- Genetic Tendency: Androgenetic alopecia has a strong genetic component that is conveyed into later generations. Because of the androgen dependency of the phenotype, the androgen receptor (AR) gene on the X-chromosome is considered a probable candidate gene for MPB.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormones can play a vital role in the development of androgenic alopecia. The hair follicle shrinks due to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which is converted from testosterone by the enzyme 5-alpha reductase.
- Age: The prevalence of male pattern baldness (MPB) increases with age, primarily affecting older adults. Factors such as geography, environment, sociology, and health contribute to shifts in the age range of MPB occurrence.
How Do You Diagnose Male Pattern Baldness?
Male pattern baldness is relatively easy to identify; hence, dermatologists begin with basic queries such as medical history, family history, hormonal problems, stress, and anxiety issues. There are some tests which include:
- Blood tests are used to diagnose medical conditions relating to hair loss, such as nutritional scarcity, thyroid diseases, etc.
- Genetic testing and examination of DNA variations to see hereditary influences.
- Scalp biopsy to identify any signs of infection or skin disease.
Proper lab analysis and examination are always necessary to recognize the root cause of the hair fall problem.
What Are the Treatment Options for Male Pattern Baldness?
There are various treatment options for androgenic alopecia. A systematic review assessed the efficacy of some possible treatments, such as:
- Minoxidil: Topical or oral minoxidil can increase blood flow to the hair follicles. It is expected to stimulate hair follicles and promote hair growth. Recent research has also uncovered an anti-androgenic effect.
- Finasteride: This medication is a type II 5α-reductase inhibitor, which means it blocks the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT). Finasteride, by preventing DHT synthesis, helps to reduce DHT levels in the scalp, which can halt the rate of hair loss and improve hair regeneration in MPB patients.
- Platelet-rich plasma (PRP): Platelet-rich plasma can reduce hair loss by increasing the growth of dermal papilla cells. Moreover, it has anti-inflammatory properties for the scalp and increases blood flow in hair follicles.
- Hair transplant: Hair transplants are by far the most effective method for male pattern baldness. It involves taking some hair from your donor area and transplanting them onto your balding area. You can get a very affordable hair transplant procedure in Turkey without breaking the bank. You can also opt to get a free consultation about your hair condition from renowned experts in this field.
The Bottom Line
Hair loss treatment can be a very demanding endeavour. Navigating the journey of male pattern baldness is never easy. It requires an understanding of the types and stages of hair loss.
First and foremost, you should give yourself time to recover and revive your hair. Among various medications, minoxidil stimulates hair growth, finasteride inhibits DHT synthesis. PRP promotes dermal papilla cell growth and increases blood flow but hair transplants are the most effective, long-term solution.
Along with medications and transplants, proper nurturing of hair, a balanced diet, a sufficient sleep cycle, a healthy lifestyle, good habits, and effective exercises can play an amazing role in defending the recession of bald spots or receding hairlines. This continuous routine can change your body clock and even your outward presentation without you even noticing! Remember, your dedication to a comprehensive routine can subtly transform not just your appearance but also your inner confidence, making the journey worthwhile.