Diffuse thinning is not a disease, but a symptom of a medical condition. About 10% of all hair diseases are cause diffuse hair loss. Diffuse thinning is a type of hair loss that usually becomes visible when more than 100 hairs a day fall out all over the head.
Visible hair shedding can occur in people of all ages and sexes. However, women are experiencing diffuse thinning ten times more than men.
There are many reasons for diffuse hair loss. Hormone levels or improper care can cause diffuse thinning. Another common cause in older women is female pattern hair loss.
Even too much of certain nutrients can cause patients to lose hair.
Female pattern hair loss - androgenetic alopecia
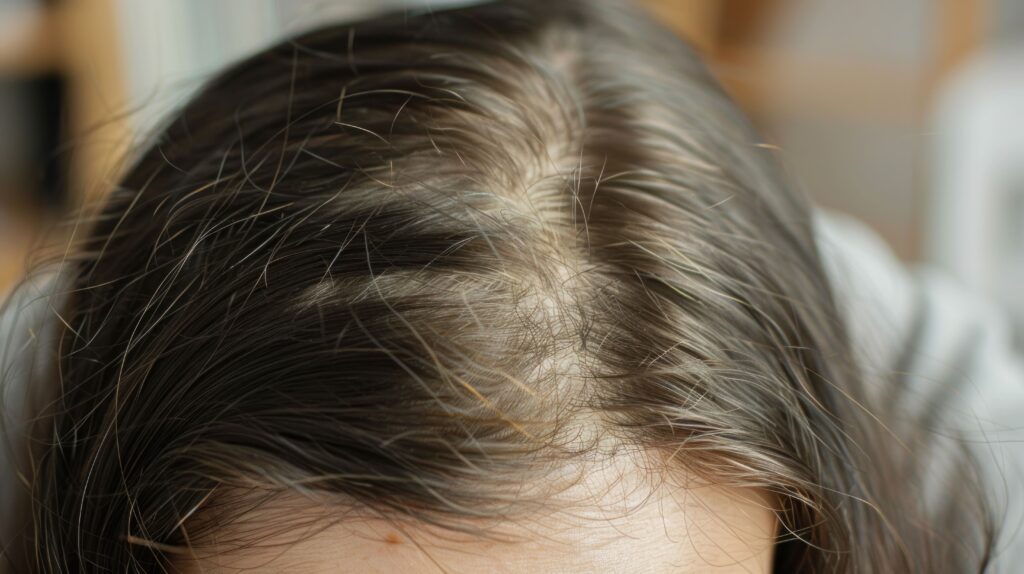

Genetics are one of the most common causes of hair loss. Male pattern hair loss is usually seen with the development of a bald patch on the top of the head or a gradually receding hairline from the temples and forehead.
Genetic hair loss in women is less common than male pattern baldness but is still frequent, especially in older women. It is often less noticeable in its early stages because it results in excessive hair loss all over the scalp. The hair thins but there are no obvious bald patches like in men.
Androgenetic alopecia is not really preventable. Genetics and hormone levels link to diffuse thinning. Both men and women have varying levels of male hormones, and some individuals’ hair follicles can be oversensitive to these hormones, leading to hair loss. The only permanent, long term solution is a hair transplant.
Diffuse alopecia, the symptoms, and its causes
Another word for hair loss is alopecia.
In diffuse thinning alopecia – in which hair falls out all over the scalp – hair falls out but the follicles remain. Therefore, theoretically, the hair can continue to grow. But thanks to whatever the cause of the hair shedding is, too many hair follicles stay in the resting phase.
Therefore, when facing hair loss that happens over the whole head, it is important to do a holistic physical examination to find the cause. Once you remove the cause, your hair will start to grow again, in contrast to androgenetic alopecia, where hair loss is typically permanent.
There is a distinction between two types of diffuse hair loss, telogen effluvium and anagen effluvium.
Telogen effluvium hair thinning
All hair follicles alternate between the resting phase and the growth phase. At the end of the telogen phase, hairs fall out, and then the growth phase starts again.
In telogen effluvium, more hairs follicles than usual enter the resting phase. This can happen intermittently or in waves.
They do not grow back if the cause for the imbalance remains in place.
The cause is often difficult to find because hair loss does not start until two to three months later. So, many patients have already forgotten what happened at that time at which hair loss was triggered.
Anagen effluvium hair thinning
In anagen effluvium, keratin production is disrupted. The hair continues to grow normally during the anagen phase, but its structure is brittle. In the worst case, the hairs break off at a length of one or two millimetres.
In this form of hair loss, hair loss occurs a few days after the damaging event. This can be the case, for example, with poisoning or with some – very aggressive – chemotherapies.
The causes of diffuse thinning
The causes of diffuse alopecia are extremely diverse. They can be divided into 4 categories:
- Local diseases of the scalp
- External damage to the scalp
- Effect of orally ingested substances (drugs, chemicals, toxins)
- General diseases or diseases of internal organs.
Examples of conditions causing diffuse hair loss include:
- Hormonal fluctuations (e.g., pregnancy)
- Thyroid disease
- Stress
- Incorrect care
- Iron deficiency or zinc deficiency
- Vitamin A poisoning
- Heavy metal poisoning
- Chemotherapy
- Radiation therapy
- Unbalanced diet/ wrong nutrition
- Anorexia/bulimia
- Side effects of medication
- Eczema on the scalp
- Mechanical effects on the hair (for example overly tight braids)
It is important to clarify the causes of diffuse alopecia with a doctor to exclude possible diseases.
A much less common form of diffuse hair loss is alopecia areata. The hair falls out in patches over the body in this auto-immune condition. A special form of the disease occurs very rarely, diffuse alopecia areata, or diffuse constitutional hair loss.
Diagnosis of thinning hair
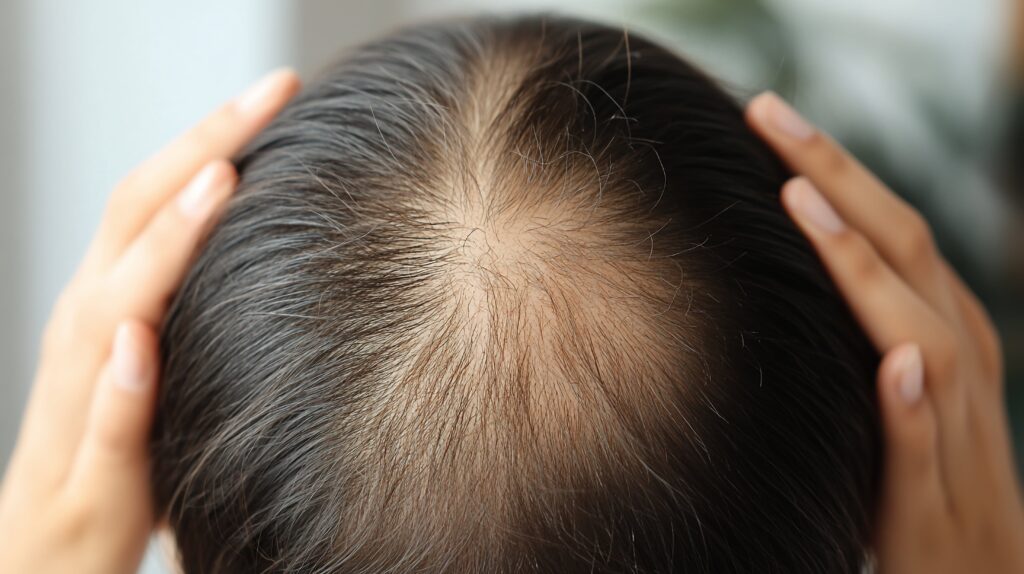
The acute variant of diffuse hair loss, known as anagen effluvium, can be resolved quickly. Hair falls out rapidly and intensely following the triggering event, allowing healthcare providers to identify the cause more easily and implement effective treatment.
The chronic variant of diffuse hair loss, telogen effluvium, is more difficult to diagnose. Hairs fall out a while after the causative event and, what is more, they do not all fall out at once. Thus, it can very difficult to diagnose what the root problem is.
Diffuse thinning can often be confused with the hair falling out in patches, such as in alopecia areata. It also needs to be separated hereditary hair loss, especially in women as female pattern baldness most closely resembles it.
Therefore, it is important to also examine the hair under the microscope so that the two diseases can be ruled out. This is because hormone treatments for genetic hair loss can be harmful to the follicles in if the cause lies elsewhere.
The treatment for diffuse thinning
The best way to cure diffuse thinning due is to remove the cause.
If the diffuse hair loss is based on a nutrient deficiency, a doctor will prescribe nutritional supplements to replenish the follicles. When the cause of diffuse hair loss is the side effect of a medication, you should consult your doctor to see if other medications are available.
If the cause is a thyroid disease, a specialist should examine and treat it. Medication such as hormones may well be necessary to deal with the cause of illness.
If the cause of diffuse hair loss is dieting, then this should be stopped immediately. In any case, anorexia and bulimia need treating by medical professionals for considerably more reasons than just hair loss.
Only hair loss that results from a disease on the scalp, such as an infection, should be treated locally. For all other causes, the solution must be found elsewhere in the body.
How long does it take for hair to grow back?
The good news is, in most cases of diffuse hair loss, the hair will grow back. This is different from androgenetic alopecia, where hair loss is permanent. So, it takes about three to six months for the hair to grow back.
Of course, hair growth can be supported with lifestyle choices, for example with a healthy diet. A good exercise routine and good all-round health will also be beneficial.
Hair transplants for diffuse thinning haur
Diffuse hair loss that is not hereditary reverses when the trigger is recognised and removed. Healthy hair then grows back again.
If the hair does not grow back, a hair transplant in Turkey may be the best option. Dr Acar and his team at Cosmedica Clinic will be happy to answer any questions you may have.
FAQ
What is diffuse thinning and who does it affect?
Diffuse thinning is a symptom of various medical conditions and occurs when over 100 hairs fall out daily from the entire scalp. It affects people of all ages and sexes; however, women experience it ten times more often than men, making it crucial to understand its underlying causes.
What causes diffuse hair thinning?
The causes of diffuse hair thinning are diverse and can include hormonal fluctuations, nutritional deficiencies, stress, and scalp conditions. External factors like medications and diet also play a significant role, making a thorough medical assessment essential for proper diagnosis and treatment.
What are the treatment options for diffuse hair thinning?
Treatment primarily focuses on addressing the underlying causes, such as nutritional deficiencies or hormonal imbalances. Consulting a doctor can help identify the right course of action, which may include supplements, medication adjustments, or lifestyle changes, leading to hair regrowth within three to six months.
