Endometriosis affects 6 to 10 percent of women worldwide. The endometrial lining tissue grows outside of the uterus and causes severe pelvic pain. It can also cause fatigue, digestive issues, irregular menstruation, and even infertility. Endometriosis primarily presents as a gynecological issue. But, endometriosis can have some systematic effects, like hair loss.
There are a variety of reasons behind endometriosis hair loss. Hormonal imbalance, inflammation, nutritional deficiencies, stress, etc., can all play a role. Unfortunately, there are no cures for endometriosis, only medication management. Sometimes, these medications can also end up disrupting your hair growth cycle. Therefore, it is crucial to understand the connection between hair loss and endometriosis.
In this article, we will talk about:
- The relationship between hair loss and endometriosis
- The reasons behind endometriosis hair loss
- The best treatments for this type of hair loss, mainly hair transplants, with Cosmedica Clinic
What is Endometriosis?
Endometriosis affects more than 190 million women around the world. It is a chronic disease starting as early as the first menstruation in girls. The main symptom of this disease is pelvic pain. In endometriosis, the uterine tissue grows outside the uterus, mainly in the pelvic area (e.g., around the ovaries or the fallopian tubes).
The inflammatory reaction is the reason for long-term physical pain. It can also cause irregular bowel movements. Endometriosis is often underdiagnosed, as the main symptom is pain. The pain is mistaken for premenstrual syndrome or gastrointestinal disorders. But can endometriosis cause hair loss?
Is Hair Loss Part of the Symptoms of Endometriosis?
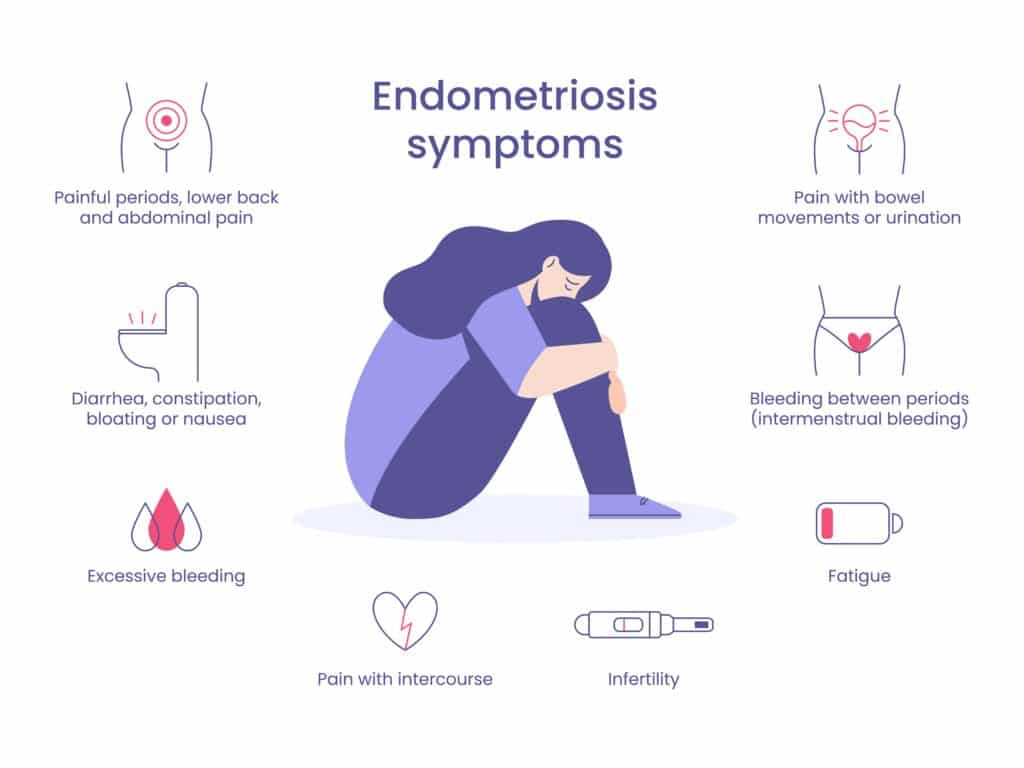
First of all, let’s look at the main symptoms caused by endometriosis. They include:
- Severe pelvic pain
- Pain during urination
- Pain during menstruation
- Pain during sexual activity
- Heavy bleeding
- Vaginal wall tenderness
- Nausea
- Fatigue
- Depression
- Infertility
Hair loss is not part of the most important symptoms of endometriosis. However it still can happen due to some hormonal imbalances caused by this condition.
What is the Treatment for Endometriosis?
Unfortunately, there is no curative treatment yet for endometriosis. Healthcare professionals only aim to manage the symptoms of the disease. Contraceptive methods or hormonal pills are used to treat endometriosis symptoms. In severe cases, surgeons might remove the uterus, ovaries, or part of the colon.
Does Endometriosis Cause Hair Loss?

Endometriosis can cause some hormonal imbalances and have a great impact on the physical and mental stress of women suffering from it. The impact the condition has on the mental and physical health can also lead to hair thinning. However, the most prominent association between endometriosis and hair loss is due to the treatment itself. Let’s look at 9 ways endometriosis can cause hair thinning:
Hormonal Imbalance can Cause Endometriosis Hair Loss
Endometriosis can lead to hair loss due to a high estrogen production in some women. A higher estrogen level can lead to female pattern hair loss. It is also known as telogen effluvium. This condition can cause diffuse hair thinning and hair loss.
Pain Medications
As endometriosis causes severe pain, sometimes patients take anti-inflammatory drugs. In some cases, some of them, like ibuprofen, can cause excess hair shedding and disturb the hair growth cycle temporarily.
Oral Contraceptives
Oral birth control pills, used to treat endometriosis’ symptoms, contain estrogen and progesterone, and these hormones can cause be linked to hair loss. Hair follicles transition from the hair growth to the resting phase, leading to hair thinning.
GnRH Agonist
Gonadotropin-releasing hormones can reduce estrogen levels. It produces menopause-like symptoms and leads to androgenic effects. In rare cases, the increase in androgen can lead to hair loss.
Aromatase Inhibitors
Aromatase inhibitors work similarly to GnRH. It creates an estrogen/androgen imbalance in your body. The imbalance can sometimes cause diffuse hair loss.
Autoimmune Disorders
Some research suggests endometriosis may have an autoimmune origin. It has genetic traits similar to those of other autoimmune conditions, such as alopecia areata, alopecia universalis, and lupus erythematosus. One study in Taiwan demonstrated that women with endometriosis were at higher risk for developing alopecia areata. A review study included the following autoimmune diseases in connection with endometriosis:
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Coeliac disease
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Autoimmune thyroid disorder
- Multiple sclerosis
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Sjögren’s syndrome
Nutrient Deficiency
Endometriosis can cause heavy vaginal bleeding. It can lead to low iron levels. Iron deficiency can decrease the oxygen supply to hair follicles. Endometriosis can also lead to low vitamin D levels. Deficiency of both iron and vitamin D can cause hair thinning.
Thyroid Function
Endometriosis can sometimes disrupt normal thyroid function. Thyroid hormones are essential to maintain healthy hair. An underactive thyroid can cause increased hair shedding.
Psychological Stress
The chronic nature of endometriosis is challenging for everyone. The stress caused by the physical pain brought on by the condition can cause diffused hair thinning. Both stress and anxiety can trigger alopecia areata or trichotillomania.
How to Care for Endometriosis Hair Loss?

Endometriosis and hair loss are not always directly associated. More often than not, hair loss is due to side effects of the underlying cause. So, it is essential to treat the underlying causes first. Let’s look at some ways you can care for endometriosis hair loss:
Medication Management
If you believe your hair loss is due to the side effect of the medication you take to treat your endometriosis, please consult with your physician. They may adjust or alter your medications. However, it would help if you did not stop taking them without consultation with your doctor.
Topical Treatments
Topical treatments like 2% or 5% minoxidil can stimulate new hair growth. However, it can not stop hair loss.
Mesotherapy
Combining derma rolling with topical minoxidil is a great way to boost new hair growth and stop existing hair loss due to endometriosis. Dermarolling can stimulate regeneration and enhance the absorption of minoxidil.
Hair Transplant to Treat Endometriosis Hair Loss
Female hair transplants are one of the most popular options for treatment-resistant hair loss. The Cosmedica Clinic has a 98% success rate in FUE hair transplants. They employ the most modern methods available at affordable rates for everyone worldwide. Unlike other treatments, their hair transplant procedures are permanent and require little maintenance.
Conclusion About Endometriosis Hair Loss
The nature of endometriosis hair loss is multifaceted. The severe pain associated with this disease can cause psychological distress in patients. Hair loss, another added symptom, is very challenging.
Therefore, you should take care of your mental health first and foremost, and it might even end up helping your hair loss issue. If your hair loss is irreversible, you can always book a consultation with Cosmedica Clinic and receive hair loss treatments today!
