Every woman goes through menopause, a natural and vital time in her life. People may notice symptoms like hot flashes and insomnia immediately, but hair loss is another less obvious sign.
Hair loss affects both men and women, but menopausal hair loss is a special concern for women because it happens when estrogen and progesterone hormones decrease. These hormones play a crucial role in determining how quickly hair grows and its appearance.
There are also genetic factors that add another layer to female pattern hair loss. In addition to genetics, extrinsic factors can also play a role, for example, stress, unhealthy diet, and specific medication.
These changes happen naturally as people age and are in line with the natural development of life. Understanding hormones, interactions of genetic factors, and how lifestyle choices affect hormones can help prevent hair loss in women. Being aware of all the different steps menopausal women go through is an essential part of dealing with hair loss.
By discussing these aspects of menopausal hair loss, we aim to enhance your comprehension of the links between hormones, hair, and overall health during this phase of life.
What is Menopausal Hair Loss?
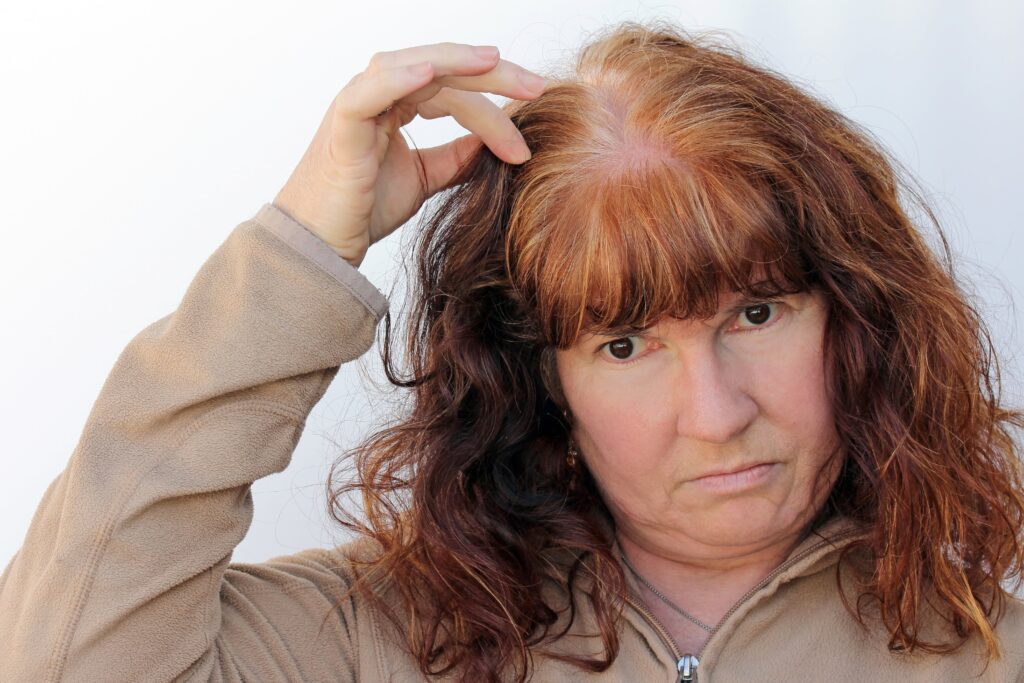

Menopause is the natural end of menstruation in a woman’s life. During menopause, estrogen and progesterone hormone levels decrease, which is part of a complex pathology of changes. Because of the menopausal hormonal cycle, hair growth slows and becomes more sensitive to androgens.
What are the Symptoms of Menopausal Hair Loss?
Menopause can lead to hair loss, and it can happen for various reasons. This phase brings about a range of symptoms and factors that can make hair changes unique for each individual. Some menopausal symptoms may include:
- Excessive Hair Fall: Menopausal hair loss often involves more hair falling out each day. Simple tasks like brushing your hair or showering might reveal increased hair loss.
- Hair Thinning: Hair thinning is a slow and often subtle sign that you are losing hair during menopause. Women might notice that their hair becomes thinner and less in various parts of their head, including the front, sides, or top.
- Changes in Hair Texture: Hormonal shifts that happen during menopause can change the way hair feels. Several women have noticed changes in the quality of their hair, making it either more fragile or prone to breakage.
Underlying Causes of the Menopausal Hair Loss
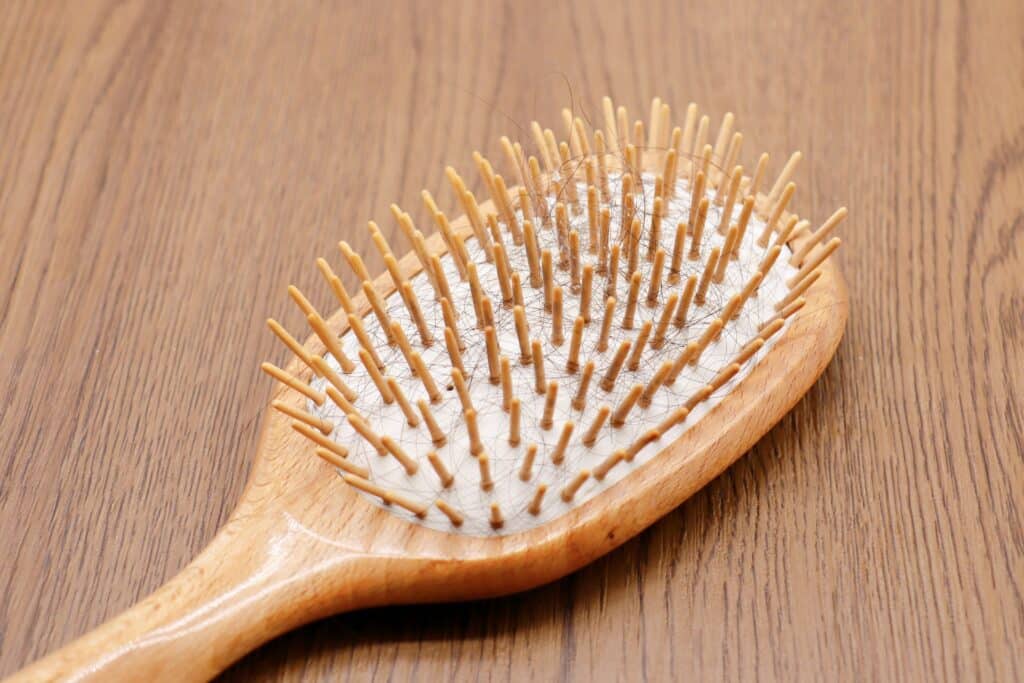

Many changes in hormones, genetics, and environmental factors cause hair loss during menopause. By looking at the root causes, you can fully understand the different parts of this complicated event.
- Less Estrogen and Progesterone: Women experience hair loss during menopause primarily because their estrogen and progesterone levels decrease. When these hormones decrease, they disrupt the hair growth cycle, leading to slower hair growth and making it more prone to damage from androgens.
- An increase in androgens: During menopause, androgens, a group of male hormones, tend to increase. This elevation can cause hair follicles to shrink, a medical condition called androgenic alopecia, contributing to hair loss.
- Genetic Predisposition: Genetic factors majorly cause hair loss during menopause. Genetics partly cause hair loss, and it’s also a natural part of aging for women.
- Illness and stress: Having a lot of stress or already having health problems can make hair loss worse during menopause. Stress lasting for a long time can throw off the balance of hormones, worsening the effects on hair growth. Diagnostic blood tests, like a complete blood count and a thyroid test, can help rule out other possible causes.
- Nutrient Deficiency: Lack of specific nutrients such as iron, calcium, and vitamin B6 can contribute to hair loss. Improving hair health through a healthy diet and essential vitamin supplements is crucial.
How to Treat Menopausal Hair Loss?
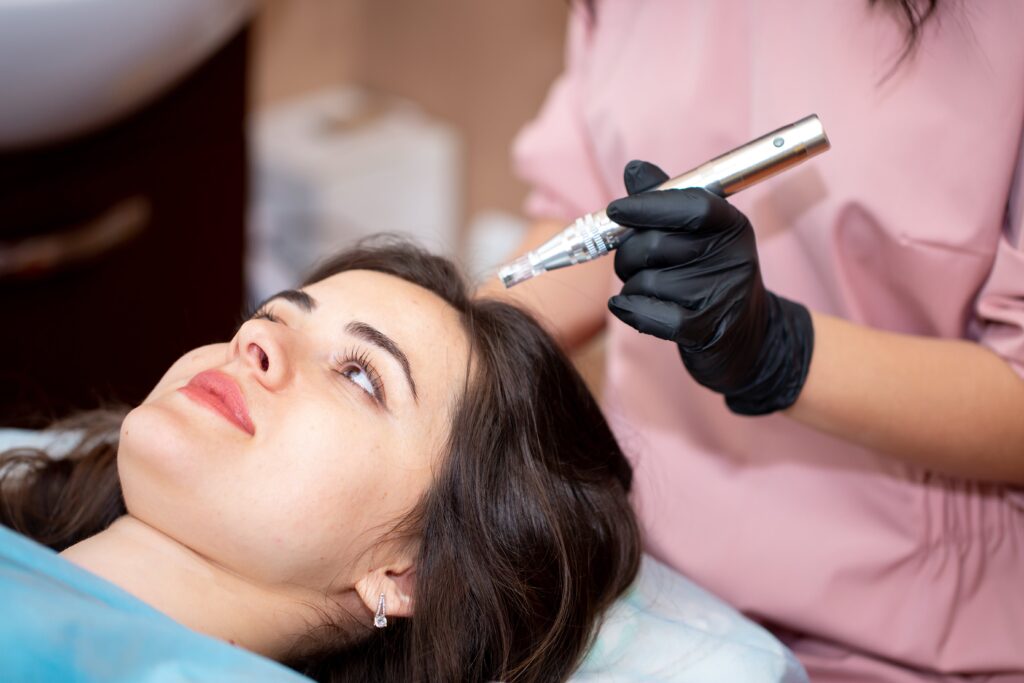
To address menopausal hair loss, it’s essential to take a well-rounded approach. This can involve hormone medications, lifestyle adjustments, and advanced treatments like hair transplantation. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Nutrient Consumption: Nutrient-rich foods with antioxidants, vitamins and minerals enhance hair health throughout menopause. Fish oil and flaxseed, rich in omega-3 fatty acids, can help prevent hair loss by promoting a healthier scalp and improving hair follicle activity. Because of their anti-inflammatory properties, these fatty acids may reduce inflammation-induced hair loss.
- Hormone Replacement Therapy: Hormone replacement treatment (HRT) can effectively mitigate menopause hair loss by rectifying hormonal imbalances, primarily by the supply of estrogen. However, there are some potential hazards and adverse reactions. So, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare practitioner before considering hormone replacement therapy for this purpose.
- Topical Treatments: If hair loss in women is due to androgens, consider using Rogaine (minoxidil) as a topical treatment to encourage hair growth. While minoxidil cannot prevent hair loss, it can promote new hair growth.
- Prescription drugs: Some prescription drugs, like finasteride and spironolactone, can help prevent menopause hair loss in women. However, there can be some adverse side effects.
- Mesotherapy: Microneedling and laser treatments are cutting-edge methods that enhance both the quality and quantity of hair. Try at-home microneedling with a mesotherapy set to improve blood circulation and promote new hair growth.
- Surgical Interventions: During menopause, hair transplantation can be a feasible solution for managing hair loss. While it can effectively address specific types of hair loss, it is imperative to consult a healthcare professional to evaluate its suitability and explore individualised remedies.
To sum-up, menopause is a natural stage in a woman’s life leading to changes, including hair loss. Hormone imbalances, genetics, and environmental factors all play a role in influencing this hair loss. It creates a unique and challenging experience for each person. Recognizing the signs, like increased hair fall, thinning, and changes in hair texture, is essential for managing this experience.
Women can avoid and manage menopause hair loss by recognising the complex relationship between hormones, genetics, and lifestyle. Women should consult with healthcare professionals to customise a treatment plan suited to their needs. Menopausal hair loss requires self-awareness, empowerment, and physical restoration.
